Questions
1
Choose the factor on which the orbital velocity does not depend when the satellite is orbiting close to the earth’s surface
Answer:The mass of the satellite
2
What happens to the gravitational potential at the centre of the uniform spherical shell which shrinks gradually?
Answer:Decreases
4
Kepler’s second law of constancy show the conservation of which of these following?
Answer:Angular momentum.
5
What is energy required to move a body of mass m from an orbit with radius 2R to 3R?
Answer:GmM/6R
6
What is ratio of linear velocities v1 and v2 of two planets which are at a distance closest and farthest from the sun? Distance from closest planet and farthest planet are d1 and d2 respectively.
Answer:(d2/d1)
7
Orbital velocity of a satellite is dependent on which factor when it is orbiting near the earth’s surface?
Answer:Radius of earth.
8
Gravitational mass of a body is proportional to the gravitational of what?
Answer:All the above.
9
What is the kinetic energy of a satellite taking time T for revolution?
Answer:T^(-2/3)
10
Which of the following proves there is a gravitational force between the earth and the sun?
Answer:Earth revolving around the sun.
11
The distance between two masses is doubled, what happens to the gravitational force between them?
Answer:Decreased to a quarter
12
The earth and the moon are subjected to the sun’s gravitational force. What does the orbit of the moon look like from the sun?
Answer:Somewhat elliptical.
14
If the gravitation effect were to be lesser than this present effect, which other force would likely to have altered?
Answer:Archimedes principle.
16
What causes tidal waves in the sea?
Answer:Gravitation effect on the earth by moon.
17
Supposing Newton’s law of gravitation for gravitation forces F1 and F2 between two masses m1 and m2 at positions r1 and r2 read
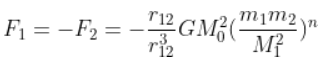
where Mo is a constant of the dimension of mass, r12 = r1 – r2 and n is a number. In such a case,
Answer:A, C, D
18
The centre of mass of an extended body on the surface of the earth and its centre of gravity
Answer:is close to each other for objects, say of sizes less than 100 m
20
There have been suggestions that the value of the gravitational constant G becomes smaller when considered over a very large time period in the future. If that happens for our earth,
Answer:C, D
Chapters
- Physical World
- Units and measurements
- Motion in a straight line
- Motion in a plane
- Laws of motion
- Work energy and power
- System of particles and rotational motion
- Gravitation
- Mechanical properties of solids
- Mechanical properties of fluids
- Thermal properties of matter
- thermodynamics
- Kinetic theory
- Oscillations
- Waves
