Questions
1
Given the following code fragment:
main()
{
int row[20],i,sum=0;
int *p=row;
for(i=0;i<20;i++)
*(p+i)=1;
for(i=0;i<20;i+=sizeof(int))
sum+=*(p+i);
printf("sum=%d\n",sum);
}
What will be the result of execution?
Answer: Option [A]
2
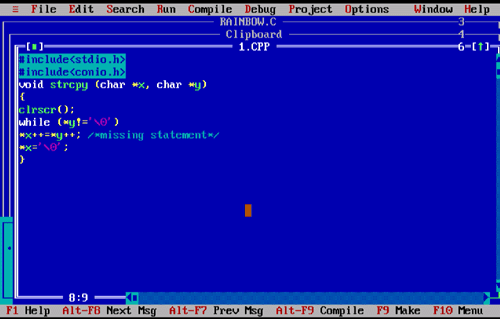
What is the missing statement in the following function which copies string x into string y?
void strcpy (char *x, char *y)
{
while (*y!='\0')
................./*missing statement*/
*x='\0';
}
What will be the result of execution?
Answer: Option [B]
Pointer variable char *x is pointing to a location and the char *y is assigned to that location. If we assume the missing statement is *x++=*y++ then both the variables point to the next respective location till null ('\0') found.
3
char *ptr; char myString[]="abcdefg"; ptr=myString ptr+=5;
The pointer ptr points to which string?
Answer: Option [A]
ptr+=5 means ptr=ptr+5
That means the pointer variable is incremented by 5. Hence it is pointing to the 6th location. i.e. fg
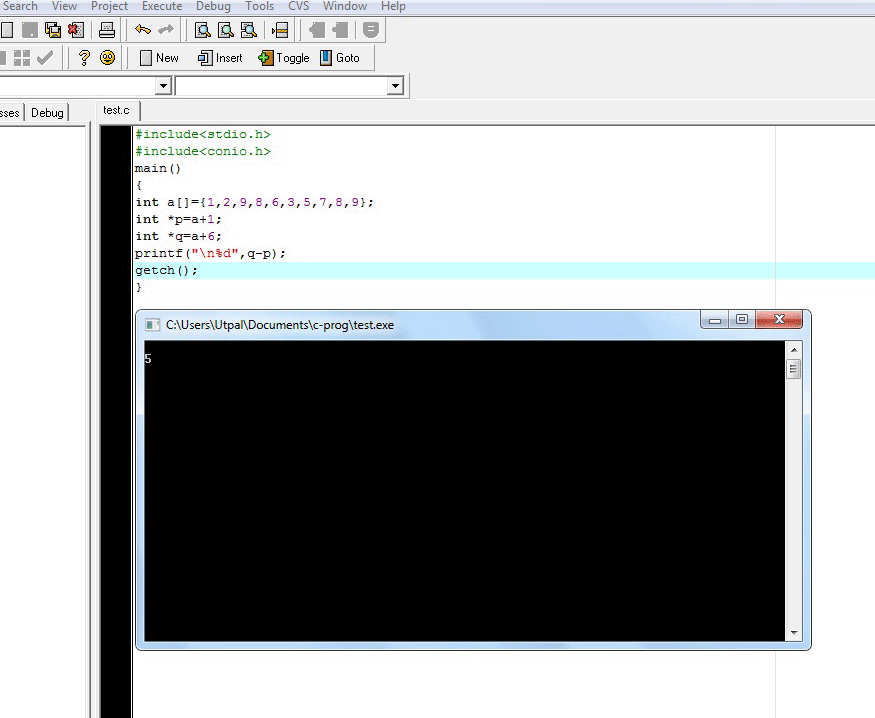
4
Output of the following program will be
main()
{
int a[]={1,2,9,8,6,3,5,7,8,9};
int *p=a+1;
int *q=a+6;
printf("\n%d",q-p);
}
Answer: Option [B]